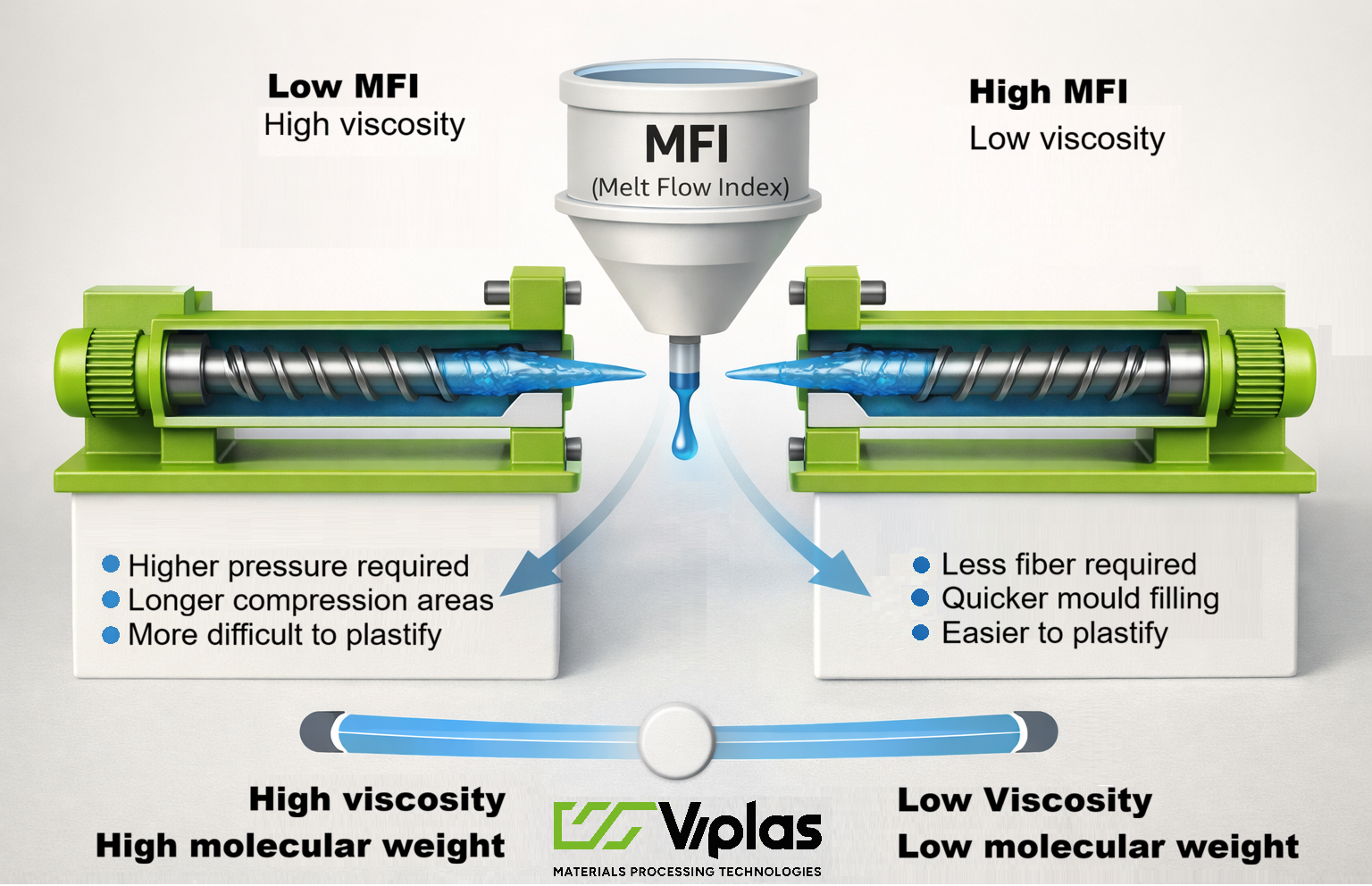
The Melt Flow Index (MFI), also known as Melt Flow Rate (MFR), is one of the fundamental parameters for the rheological characterization of thermoplastic plastic materials.
It represents the mass of molten polymer that flows through a standard nozzle in 10 minutes, at a given temperature and under a defined load, according to international standards (ISO 1133, ASTM D1238).
The unit of measurement of MFI is g/10 min.
From a physical point of view, the MFI is inversely proportional to the viscosity of the molten material and provides an indirect indication of the average molecular weight of the polymer:
• Low MFI → high viscosity → high molecular weight
• High MFI → low viscosity → lower molecular weight
Influence of the MFI on the transformation process
The MFI value has a direct impact on the behavior of the material during transformation and therefore on the stability of the process, the quality of the product and the operating conditions of the machine.
Low MFI materials (more viscous polymers)
• Require higher torques and pressures
• They present greater resistance to flow
• They allow better dimensional stability of the melt
• They are typically used in:
- extrusion of tubes and profiles
- blowing (bottles, cans)
- structural applications
High MFI materials (more fluid polymers)
• Flow more easily
• They allow rapid filling of the moulds
• Require lower pressures
• They are preferred for:
- injection molding
- complex geometries
- thin walls
Relationship between MFI and plasticization screw:
Low MFI materials
• They need:
- screws with greater capacity to generate pressure
- more effective compression zones
• Often require:
- higher compression ratios
- optimized screw profiles to improve casting
• Inefficient lamination can lead to:
- overheating
- flow instability
- variations in flow rate
High MFI materials
• They are easier to laminate
• They require:
- less mechanical energy
- accurate temperature control to avoid degradation
• Too aggressive screws can cause:
- excessive shear
- thermal degradation of the polymer
- loss of mechanical properties
Effects of MFI on product quality
Correct selection of the MFI is essential to achieve the right balance between:
• processability
• mechanical performance
• surface quality
• dimensional stability
In particular:
• Too high MFI can cause:
- drippings
- poor mechanical resistance
- deformations
• Too low MFI can lead to:
- difficulty filling
- process instability
- increase in energy consumption
Conclusions
The Melt Flow Index is not just a data sheet data, but a key process design parameter.
The correct interpretation of the MFI allows you to:
• choose the most suitable material for the application
• optimize the design of the plasticizing screw
• improve stability, quality and repeatability of the production process
An integrated approach between material, screw and process parameters is essential to fully exploit the potential of the polymer and the plant.